Information Security
Information security means protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.The terms information security, computer security and information assurance are frequently used interchangeably. These fields are interrelated and share the common goals of protecting the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information; however, there are some subtle differences between them. These differences lie primarily in the approach to the subject, the methodologies used, and the areas of concentration. Information security is concerned with the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data regardless of the form the data may take: electronic, print, or other forms.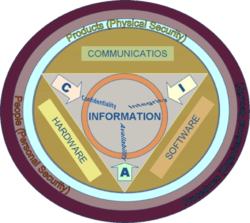



Governments, military, financial institutions, hospitals, and private businesses amass a great deal of confidential information about their employees, customers, products, research, and financial status. Most of this information is now collected, processed and stored on electronic computers and transmitted across networks to other computers. Should confidential information about a businesses customers or finances or new product line fall into the hands of a competitor, such a breach of security could lead to lost business, law suits or even bankruptcy of the business. Protecting confidential information is a business requirement, and in many cases also an ethical and legal requirement. For the individual, information security has a significant effect on Privacy, which is viewed very differently in different cultures.
The field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. As a career choice there are many ways of gaining entry into the field. It offers many areas for specialization including Information Systems Auditing, Business Continuity Planning and Digital Forensics Science, to name a few.
This article presents a general overview of information security and its core concepts.
History
This article will not attempt to provide a comprehensive history of the field of information security, rather it will suffice to describe the earliest roots and key developments of what is now known as information security.
Since the early days of writing, heads of state and military commanders understood that it was necessary to provide some mechanism to protect the confidentiality of written correspondence and to have some means of detecting tampering. Persons desiring secure communications have used wax seals and other sealing devices since the early days of writing to signify the authenticity of documents, prevent tampering, and ensure confidentiality of correspondence.
Julius Caesar is credited with the invention of the Caesar cipher c50 B.C. to prevent his secret messages from being read should a message fall into the wrong hands.
World War II brought about many advancements in information security and may mark the beginning of information security as a professional field. WWII saw advancements in the physical protection of information with barricades and armed guards controlling access into information centers. It also saw the introduction of formalized classification of data based upon the sensitivity of the information and who could have access to the information.During WWII background checks were also conducted before granting clearance to classified information.
The end of the 20th century and early years of the 21st century saw rapid advancements in telecommunications, computing hardware and software, and data encryption. The availability of smaller, more powerful and less expensive computing equipment made electronic data processing within the reach of small business and the home user. These computers quickly became interconnected through a network generically called the Internet or World Wide Web.
The rapid growth and wide spread use of electronic data processing and electronic business conducted through the Internet, along with numerous occurrences of international terrorism, fueled the need for better methods of protecting these computers and the information they store, process and transmit. The academic disciplines of computer security, information security and information assurance emerged along with numerous professional organizations - all sharing the common goals of insuring the security and reliability of information systems.
Basic principles
Key concepts
For over twenty years information security has held that confidentiality, integrity and availability (known as the CIA Triad) are the core principles of information security.

Confidentiality
Confidentiality of information is present, when disclosure or exposure to unauthorized individuals or systems is prevented. For example, it is virtually impossible to get a drivers license, rent an apartment, obtain medical care, or take out a loan without disclosing a great deal of very personal information about ourselves, such as our name, address, telephone number, date of birth, Social Security number, marital status, number of children, mother’s maiden name, income, place of employment, medical history, etc. This is all very personal and private information, yet we are often required to provide such information in order to transact business. We generally take it on faith that the person, business, or institution to whom we disclose such personal information have taken measures to ensure that our information will be protected from unauthorized disclosure, either accidental or intentional, and that our information will only be shared with other people, businesses or institutions who are authorized to have access to the information and who have a genuine need to know the information.
Information that is considered to be confidential in nature must only be accessed, used, copied, or disclosed by persons who have been authorized to do so, and only when there is a genuine need to do so. A breach of confidentiality occurs when information that is considered to be confidential in nature has been, or may have been, accessed, used, copied, or disclosed to, or by, someone who was not authorized to have access to the information.
For example: permitting someone to look over your shoulder at your computer screen while you have confidential data displayed on it would be a breach of confidentiality if they were not authorized to have the information. If a laptop computer, which contains employment and benefit information about 100,000 employees, is stolen from a car (or is sold on eBay) could result in a breach of confidentiality because the information is now in the hands of someone who is not authorized to have it. Giving out confidential information over the telephone is a breach of confidentiality if the caller is not authorized to have the information.
Confidentiality is necessary (but not sufficient) for maintaining the privacy of the people whose personal information the organization holds.
Integrity
In information security, integrity means that data can not be created, changed, or deleted without authorization. It also means that data stored in one part of a database system is in agreement with other related data stored in another part of the database system (or another system). For example: a loss of integrity can occur when a database system is not properly shut down before maintenance is performed or the database server suddenly loses electrical power . A loss of integrity occurs when an employee accidentally, or with malicious intent, deletes important data files. A loss of integrity can occur if a computer virus is released onto the computer. A loss of integrity can occur when an on-line shopper is able to change the price of the product they are purchasing.
Possession
The possession is a quality or state of having ownership or control of some object or item.An information is said to be one’s possession if one obtain it ,independent of format and other characteristics.
Availability
The concept of availability means that the information, the computing systems used to process the information, and the security controls used to protect the information are all available and functioning correctly when the information is needed. The opposite of availability is denial of service (DOS).
In 2002, Mr. Donn Parker proposed an alternative model for the classic CIA triad that he called the six atomic elements of information. His alternative model includes confidentiality, possession or control, integrity, authenticity, availability, and utility. The merits of the Parkerian hexad are a subject of debate amongst security professionals.
Authenticity
In computing, e-Business and information security it is necessary to ensure that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine (i.e. they have not been forged or fabricated.)
Non-repudiation
In law, non-repudiation implies ones intention to fulfill their obligations to a contract. It also implies that one party of a transaction can not deny having received a transaction nor can the other party deny having sent a transaction.
Electronic commerce uses technology such as digital signatures and encryption to establish authenticity and non-repudiation.
Risk management
A comprehensive treatment of the topic of risk management is beyond the scope of this article. We will however, provide a useful definition of risk management, outline a commonly used process for risk management, and define some basic terminology.
The CISA Review Manual 2006 provides the following definition of risk management: “Risk management is the process of identifying vulnerabilities and threats to the information resources used by an organization in achieving business objectives, and deciding what countermeasures, if any, to take in reducing risk to an acceptable level, based on the value of the information resource to the organization.”
There are two things in this definition that may need some clarification. First, the process of risk management is an ongoing iterative process. It must be repeated indefinitely. The business environment is constantly changing and new threats and vulnerabilities emerge every day. Second, the choice of countermeasures (controls) used to manage risks must strike a balance between productivity, cost, effectiveness of the countermeasure, and the value of the informational asset being protected.
Risk is the likelihood that something bad will happen that causes harm to an informational asset (or the loss of the asset). A vulnerability is a weakness that could be used to endanger or cause harm to an informational asset. A threat is anything (man made or act of nature) that has the potential to cause harm.
The likelihood that a threat will use a vulnerability to cause harm creates a risk. When a threat does use a vulnerability to inflict harm, it has an impact. In the context of information security, the impact is a loss of availability, integrity, and confidentiality, and possibly other losses (lost income, loss of life, loss of real property). It should be pointed out that it is not possible to identify all risks, nor is it possible to eliminate all risk. The remaining risk is called residual risk.
A risk assessment is carried out by a team of people who have knowledge of specific areas of the business. Membership of the team may vary over time as different parts of the business are assessed. The assessment may use a subjective qualitative analysis based on informed opinion, or where reliable dollar figures and historical information is available, the analysis may use quantitative analysis.
The ISO/IEC 27002:2005 Code of practice for information security management recommends the following be examined during a risk assessment:
- security policy,
- organization of information security,
- asset management, human resources security,
- physical and environmental security,
- communications and operations management,
- access control,
- information systems acquisition,
- development and maintenance,
- information security incident management,
- business continuity management, and
- regulatory compliance.
In broad terms the risk management process consists of:
- Identification of assets and estimating their value. Include: people, buildings, hardware, software, data (electronic, print, other), supplies.
- Conduct a threat assessment. Include: Acts of nature, acts of war, accidents, malicious acts originating from inside or outside the organization.
- Conduct a vulnerability assessment, and for each vulnerability, calculate the probability that it will be exploited. Evaluate policies, procedures, standards, training, physical security, quality control, technical security.
- Calculate the impact that each threat would have on each asset. Use qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis.
- Identify, select and implement appropriate controls. Provide a proportional response. Consider productivity, cost effectiveness, and value of the asset.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the control measures. Ensure the controls provide the required cost effective protection without discernible loss of productivity.
For any given risk, Executive Management can choose to accept the risk based upon the relative low value of the asset, the relative low frequency of occurrence, and the relative low impact on the business. Or, leadership may choose to mitigate the risk by selecting and implementing appropriate control measures to reduce the risk. In some cases, the risk can be transferred to another business by buying insurance or out-sourcing to another business. The reality of some risks may be disputed. In such cases leadership may choose to deny the risk. This is itself a potential risk.
Controls
When Management chooses to mitigate a risk, they will do so by implementing one or more of three different types of controls.
Administrative
Administrative controls (also called procedural controls) consist of approved written policies, procedures, standards and guidelines. Administrative controls form the framework for running the business and managing people. They inform people on how the business is to be run and how day to day operations are to be conducted. Laws and regulations created by government bodies are also a type of administrative control because they inform the business. Some industry sectors have policies, procedures, standards and guidelines that must be followed - the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard required by Visa and Master Card is such an example. Other examples of administrative controls include the corporate security policy, password policy, hiring policies, and disciplinary policies.
Administrative controls form the basis for the selection and implementation of logical and physical controls. Logical and physical controls are manifestations of administrative controls. Administrative controls are of paramount importance.
Logical
Logical controls (also called technical controls) use software and data to monitor and control access to information and computing systems. For example: passwords, network and host based firewalls, network intrusion detection systems, access control lists, and data encryption are logical controls.
An important logical control that is frequently overlooked is the principle of least privilege. The principle of least privilege requires that an individual, program or system process is not granted any more access privileges than are necessary to perform the task. A blatant example of the failure to adhere to the principle of least privilege is logging into Windows as user Administrator to read Email and surf the Web. Violations of this principle can also occur when an individual collects additional access privileges over time. This happens when employees’ job duties change, or they are promoted to a new position, or they transfer to another department. The access privileges required by their new duties are frequently added onto their already existing access privileges which may no longer be necessary or appropriate.
Physical
Physical controls monitor and control the environment of the work place and computing facilities. They also monitor and control access to and from such facilities. For example: doors, locks, heating and air conditioning, smoke and fire alarms, fire suppression systems, cameras, barricades, fencing, security guards, cable locks, etc. Separating the network and work place into functional areas are also physical controls.
An important physical control that is frequently overlooked is the separation of duties. Separation of duties ensures that an individual can not complete a critical task by himself. For example: an employee who submits a request for reimbursement should not also be able to authorize payment or print the check. An applications programmer should not also be the server administrator or the database administrator - these roles and responsibilities must be separated from one another.
Security classification for information
An important aspect of information security and risk management is recognizing the value of information and defining appropriate procedures and protection requirements for the information. Not all information is equal and so not all information requires the same degree of protection. This requires information to be assigned a security classification.
The first step in information classification is to identify a member of senior management as the owner of the particular information to be classified. Next, develop a classification policy. The policy should describe the different classification labels, define the criteria for information to be assigned a particular label, and list the required security controls for each classification.
Some factors that influence which classification information should be assigned include how much value that information has to the organization, how old the information is and whether or not the information has become obsolete. Laws and other regulatory requirements are also important considerations when classifying information.
Common information security classification labels used by the business sector are: public, sensitive, private, confidential. Common information security classification labels used by government are: Unclassified, Sensitive But Unclassified, Restricted, Confidential, Secret, Top Secret and their non-English equivalents.
All employees in the organization, as well as business partners, must be trained on the classification schema and understand the required security controls and handling procedures for each classification. The classification a particular information asset has been assigned should be reviewed periodically to ensure the classification is still appropriate for the information and to ensure the security controls required by the classification are in place.
Access control
Access to protected information must be restricted to people who are authorized to access the information. The computer programs, and in many cases the computers that process the information, must also be authorized. This requires that mechanisms be in place to control the access to protected information. The sophistication of the access control mechanisms should be in parity with the value of the information being protected - the more sensitive or valuable the information the stronger the control mechanisms need to be. The foundation on which access control mechanisms are built start with identification and authentication.
Identification is an assertion of who someone is or what something is. If a person makes the statement “Hello, my name is John Doe.” they are making a claim of who they are. However, their claim may or may not be true. Before John Doe can be granted access to protected information it will be necessary to verify that the person claiming to be John Doe really is John Doe.
Authentication is the act of verifying a claim of identity. When John Doe goes into a bank to make a withdrawal, he tells the bank teller he is John Doe (a claim of identity). The bank teller asks to see a photo ID, so he hands the teller his drivers license. The bank teller checks the license to make sure it has John Doe printed on it and compares the photograph on the license against the person claiming to be John Doe. If the photo and name match the person, then the teller has authenticated that John Doe is who he claimed to be.
There are three different types of information that can be used for authentication: something you know, something you have, or something you are. Examples of something you know include such things as a PIN, a password, or your mothers maiden name. Examples of something you have include a drivers license or a magnetic swipe card. Something you are refers to biometrics. Examples of biometrics include palm prints, finger prints, voice prints and retina (eye) scans. Strong authentication requires providing information from two of the three different types of authentication information. For example, something you know plus something you have. This is called two factor authentication.
On computer systems in use today, the Username is the most common form of identification and the Password is the most common form of authentication. Usernames and passwords have served their purpose but in our modern world they are no longer adequate. Usernames and passwords are slowly being replaced with more sophisticated authentication mechanisms.
After a person, program or computer has successfully been identified and authenticated then it must be determined what informational resources they are permitted to access and what actions they will be allowed to perform (run, view, create, delete, or change). This is called authorization.
Authorization to access information and other computing services begins with administrative policies and procedures. The polices prescribe what information and computing services can be accessed, by whom, and under what conditions. The access control mechanisms are then configured to enforce these policies.
Different computing systems are equipped with different kinds of access control mechanisms, some may offer a choice of different access control mechanisms. The access control mechanism a system offers will be based upon one of three approaches to access control or it may be derived from a combination of the three approaches.
The non-discretionary approach consolidates all access control under a centralized administration. The access to information and other resources is usually based on the individuals function (role) in the organization or the tasks the individual must perform. The discretionary approach gives the creator or owner of the information resource the ability to control access to those resources. In the Mandatory access control approach, access is granted or denied bases upon the security classification assigned to the information resource.
Examples of common access control mechanisms in use today include Role-based access control available in many advanced Database Management Systems, simple file permissions provided in the UNIX and Windows operating systems, Group Policy Objects provided in Windows network systems, Kerberos, RADIUS, TACACS, and the simple access lists used in many firewalls and routers.
To be effective, policies and other security controls must be enforceable and upheld. Effective policies ensure that people are held accountable for their actions. All failed and successful authentication attempts must be logged, and all access to information must leave some type of audit trail.
Cryptography
Information security uses cryptography to transform usable information into a form that renders it unusable by anyone other than an authorized user; this process is called encryption. Information that has been encrypted (rendered unusable) can be transformed back into its original usable form by an authorized user, who possesses the cryptographic key, through the process of decryption. Cryptography is used in information security to protect information from unauthorized or accidental discloser while the information is in transit (either electronically or physically) and while information is in storage.
Cryptography provides information security with other useful applications as well including improved authentication methods, message digests, digital signatures, non-repudiation, and encrypted network communications. Older less secure application such as telnet and ftp are slowly being replaced with more secure applications such as ssh that use encrypted network communications. Wireless communications can be encrypted using the WPA protocol. Software applications such as GNUPG or PGP can be used to encrypt data files and Email.
Cryptography can introduce security problems when it is not implemented correctly. Cryptographic solutions need to be implemented using industry accepted solutions that have undergone rigorous peer review by independent experts in cryptography. The length and strength of the encryption key is also an important consideration. A key that is weak or too short will produce weak encryption. The keys used for encryption and decryption must be protected with the same degree of rigor as any other confidential information. They must be protected from unauthorized disclosure and destruction and they must be available when needed. PKI solutions address many of the problems that surround key management.
Defense in depth
Information security must protect information throughout the life span of the information, from the initial creation of the information on through to the final disposal of the information. The information must be protected while in motion and while at rest. During its life time, information may pass through many different information processing systems and through many different parts of information processing systems. There are many different ways the information and information systems can be threatened. To fully protect the information during its lifetime, each component of the information processing system must have its own protection mechanisms. The building up, layering on and overlapping of security measures is called defense in depth. The strength of any system is no greater than its weakest link. Using a defence in depth strategy, should one defensive measure fail there are other defensive measures in place that continue to provide protection.
 Recall the earlier discussion about administrative controls, logical controls, and physical controls. The three types of controls can be used to form the bases upon which to build a defence-in depth-strategy. With this approach, defence in depth can be conceptualised as three distinct layers or planes laid one on top of the other. Additional insight into defence in depth can be gained by thinking of it as forming the layers of an onion, with data at the core of the onion, people as the outer layer of the onion, and network security, host-based security and applications security forming the inner layers of the onion. Both perspectives are equally valid and each provides valuable insight into the implementation of a good defence-in-depth strategy.
Recall the earlier discussion about administrative controls, logical controls, and physical controls. The three types of controls can be used to form the bases upon which to build a defence-in depth-strategy. With this approach, defence in depth can be conceptualised as three distinct layers or planes laid one on top of the other. Additional insight into defence in depth can be gained by thinking of it as forming the layers of an onion, with data at the core of the onion, people as the outer layer of the onion, and network security, host-based security and applications security forming the inner layers of the onion. Both perspectives are equally valid and each provides valuable insight into the implementation of a good defence-in-depth strategy. Process
The terms reasonable and prudent person, due care and due diligence have been used in the fields of Finance, Securities, and Law for many years. In recent years these terms have found their way into the fields of computing and information security. U.S.A. Federal Sentencing Guidelines now make it possible to hold corporate officers liable for failing to exercise due care and due diligence in the management of their information systems.
In the business world, stockholders, customers, business partners and governments have the expectation that corporate officers will run the business in accordance with accepted business practices and in compliance with laws and other regulatory requirements. This is often described as the “reasonable and prudent person” rule. A prudent person takes due care to ensure that everything necessary is done to operate the business by sound business principles and in a legal ethical manner. A prudent person is also diligent (mindful, attentive, and ongoing) in their due care of the business.
In the field of Information Security, Harris offers the following definitions of due care and due diligence:
“Due care are steps that are taken to show that a company has taken responsibility for the activities that take place within the corporation and has taken the necessary steps to help protect the company, its resources, and employees.” And, [Due diligence are the] “continual activities that make sure the protection mechanisms are continually maintained and operational.”
Attention should be made to two important points in these definitions. First, in due care, steps are taken to show - this means that the steps can be verified, measured, or even produce tangible artifacts. Second, in due diligence, there are continual activities - this means that people are actually doing things to monitor and maintain the protection mechanisms, and these activities are ongoing.
Security governance
The Software Engineering Institute (SEI) at Carnegie Mellon University, in a publication titled “Governing for Enterprise Security (GES)”, defines characteristics of effective security governance. These include:
- An Enterprise-wide Issue.
- Leaders are Accountable.
- Viewed as a Business Requirement.
- Risk-based.
- Roles, Responsibilities, and Segregation of Duties Defined.
- Addressed and Enforced in Policy.
- Adequate Resources Committed.
- Staff Aware and Trained.
- A Development Life Cycle Requirement.
- Planned, Managed, Measurable, and Measured.
- Reviewed and Audited.
Incident response plans
- Selecting team members
- Define roles, responsibilities and lines of authority
- Define a security incident
- Define a reportable incident
- Training
- Detection
- Classification
- Escalation
- Containment
- Eradication
- Documentation
Change management
Change management is a formal process for directing and controlling alterations to the information processing environment. This includes alterations to desktop computers, the network, servers and software. The objectives of change management are to reduce the risks posed by changes to the information processing environment and improve the stability and reliability of the processing environment as changes are made. It is not the objective of change management to prevent or hinder necessary changes from being implemented.
Any change to the information processing environment introduces an element of risk. Even apparently simple changes can have unexpected effects. One of Managements many responsibilities is the management of risk. Change management is a tool for managing the risks introduced by changes to the information processing environment. Part of the change management process ensures that changes are not implemented at inopportune times when they may disrupt critical business processes or interfere with other changes being implemented.
Not every change needs to be managed. Some kinds of changes are a part of the everyday routine of information processing and adhere to a predefined procedure, which reduces the overall level of risk to the processing environment. Creating a new user account or deploying a new desktop computer are examples of changes that do not generally require change management. However, relocating user file shares, or upgrading the Email server pose a much higher level of risk to the processing environment and are not a normal everyday activity. The critical first steps in change management are (i) defining change (and communicating that definition) and (b) defining the scope of the change system.
Change management is usually overseen by a Change Review Board comprised of representatives from key business areas, security, networking, systems administrators, Database administration, applications development, desktop support and the help desk. The tasks of the Change Review Board can be facilitated with the use of automated work flow application. The responsibility of the Change Review Board is to ensure the organizations documented change management procedures are followed. The change management process is as follows:
- Requested: Anyone can request a change. The person making the change request may or may not be the same person that performs the analysis or implements the change. When a request for change is received, it may undergo a preliminary review to determine if the requested change is compatible with the organizations business model and practices, and to determine the amount of resources needed to implement the change.
- Approved: Management runs the business and controls the allocation of resources therefore, Management must approve requests for changes and assign a priority for every change. Management might choose to reject a change request if the change is not compatible with the business model, industry standards or best practices. Management might also choose to reject a change request if the change requires more resources than can be allocated for the change.
- Planned Planning a change involves discovering the scope and impact of the proposed change; analyzing the complexity of the change; allocation of resources and, developing, testing and documenting both implementation and backout plans. Need to define the criteria on which a decision to backout will be made.
- Tested: Every change must be tested in a safe test environment, which closely reflects the actual production environment, before the change is applied to the production environment. The backout plan must also be tested.
- Scheduled: Part of the change review board’s responsibility is to assist in the scheduling of changes by reviewing the proposed implementation date for potential conflicts with other scheduled changes or critical business activities.
- Communicated: Once a change has been scheduled it must be communicated. The communication is to give others the opportunity to remind the change review board about other changes or critical business activities that might have been overlooked when scheduling the change. The communication also serves to make the Help Desk and users aware that a change is about to occur. Another responsibility of the change review board is to ensure that scheduled changes have been properly communicated to those who will be affected by the change or otherwise have an interest in the change.
- Implemented: At the appointed date and time, the changes must be implemented. Part of the planning process was to develop an implementation plan, testing plan and, a back out plan. If the implementation of the change should fail or, the post implementation testing fails or, other “drop dead” criteria have been met, the back out plan should be implemented.
- Documented: All changes must be documented. The documentation includes the initial request for change, its approval, the priority assigned to it, the implementation, testing and back out plans, the results of the change review board critique, the date/time the change was implemented, who implemented it, and whether the change was implemented successfully, failed or postponed.
- Post change review: The change review board should hold a post implementation review of changes. It is particularly important to review failed and backed out changes. The review board should try to understand the problems that were encountered, and look for areas for improvement.
Change management procedures that are simple to follow and easy to use can greatly reduce the overall risks created when changes are made to the information processing environment. Good change management procedures improve the over all quality and success of changes as they are implemented. This is accomplished through planning, peer review, documentation and communication.
Disaster recovery planning
- What is Disaster Recovery Planning
- How are DRP and BCP different
- How are DRP and BCP related
- Project leader
- Identify key stake holders
- Identify key assets
- Prioritize key business functions and key asset
- Review current status for adequacy
- Make a plan
Laws and regulations
Below is a partial listing of European, United Kingdom, Canadian and USA governmental laws and regulations that have, or will have, a significant effect on data processing and information security. Important industry sector regulations have also been included when they have a significant impact on information security.
- UK Data Protection Act 1998 makes new provisions for the regulation of the processing of information relating to individuals, including the obtaining, holding, use or disclosure of such information. The European Union Data Protection Directive (EUDPD) requires that all EU member must adopt national regulations to standardize the protection of data privacy for citizens throughout the EU.
- The Computer Misuse Act 1990 is an Act of the UK Parliament making computer crime (e.g. hacking) a criminal offence. The Act has become a model upon which several other countries including Canada and the Republic of Ireland, have drawn inspiration when subsequently drafting their own information security laws.
- EU Data Retention laws requires Internet service providers and phone companies to keep data on every electronic message sent and phone call made for between six months and two years.
- The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) (20 U.S.C. § 1232 g; 34 CFR Part 99) is a USA Federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. The law applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicable program of the U.S. Department of Education. Generally, schools must have written permission from the parent or eligible student in order to release any information from a student’s education record.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires the adoption of national standards for electronic health care transactions and national identifiers for providers, health insurance plans, and employers. And, it requires health care providers, insurance providers and employers to safeguard the security and privacy of health data.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act of 1999(GLBA), also know as the Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999, protects the privacy and security of private financial information that financial institutions collect, hold, and process.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX). Section 404 of the act requires publicly traded companies to assess the effectiveness of their internal controls for financial reporting in annual reports they submit at the end of each fiscal year. Chief information officers are responsible for the security, accuracy and the reliability of the systems that manage and report the financial data. The act also requires publicly traded companies to engage independent auditors who must attest to, and report on, the validity of their assessments.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) establishes comprehensive requirements for enhancing payment account data security. It was developed by the founding payment brands of the PCI Security Standards Council, including American Express, Discover Financial Services, JCB, MasterCard Worldwide and Visa International, to help facilitate the broad adoption of consistent data security measures on a global basis. The PCI DSS is a multifaceted security standard that includes requirements for security management, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design and other critical protective measures.
- State Security Breach Notification Laws (California and many others) require businesses, nonprofits, and state institutions to notify consumers when unencrypted “personal information” may have been compromised, lost, or stolen.
- Personal Information Protection and Electronics Document Act (PIPEDA) - An Act to support and promote electronic commerce by protecting personal information that is collected, used or disclosed in certain circumstances, by providing for the use of electronic means to communicate or record information or transactions and by amending the Canada Evidence Act, the Statutory Instruments Act and the Statute Revision ActThant is in fact the case.
Sources of standards
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is a consortium of national standards institutes from 157 countries with a Central Secretariat in Geneva Switzerland that coordinates the system. The ISO is the world’s largest developer of standards. The ISO-15443: “Information technology - Security techniques - A framework for IT security assurance”, ISO-17799: “Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security management”, ISO-20000: “Information technology - Service management”, and ISO-27001: “Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems” are of particular interest to information security professionals.
The USA National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Commerce Department’s Technology Administration. The NIST Computer Security Division develops standards, metrics, tests and validation programs as well as publishes standards and guidelines to increase secure IT planning, implementation, management and operation. NIST is also the custodian of the USA Federal Information Processing Standardpublications (FIPS)].
The Internet Society (ISOC) is a professional membership society with more than 100 organization and over 20,000 individual members in over 180 countries. It provides leadership in addressing issues that confront the future of the Internet, and is the organization home for the groups responsible for Internet infrastructure standards, including the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the Internet Architecture Board (IAB). The ISOC hosts the Requests for Comments (RFCs) which includes the Official Internet Protocol Standards and the RFC-2196 Site Security Handbook.
The Information Security Forum is a global nonprofit organization of several hundred leading organizations in financial services, manufacturing, telecommunications, consumer goods, government, and other areas. It provides research into best practice and practice advice summarized in its biannual Standard of Good Practice, incorporating detail specifications across many areas.
Professionalism
In 1989, Carnegie Mellon University established the Information Networking Institute, the United State’s first research and education center devoted to information networking. The academic disciplines of computer security, information security and information assurance emerged along with numerous professional organizations during the later years of the 20th century and early years of the 21st century.
Entry into the field can be accomplished through self-study, college or university schooling in the field, or through week long focused training camps. Many colleges, universities and training companies offer many of their programs on- line. The GIAC-GSEC and Security+ certifications are both respected entry level security certifications. Membership of the Institute of Information Security Professionals (IISP) is gaining traction in the U.K. as the professional standard for Information Security Professionals.
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is a well respected mid- to senior-level information security certification. The Information Systems Security Architecture Professional (ISSAP), Information Systems Security Engineering Professional (ISSEP), and Information Systems Security Management Professional (ISSMP) certifications are well-respected advanced certifications in information-security architecture, engineering, and management respectively.
The profession of information security has seen an increased demand for security professionals who are experienced in network security auditing, penetration testing, and digital forensics investigation.
Conclusion
Information security is the ongoing process of exercising due care and due diligence to protect information, and information systems, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, destruction, modification, or disruption or distribution. The never ending process of information security involves ongoing training, assessment, protection, monitoring & detection, incident response & repair, documentation, and review.
Further reading
- Anderson, K., “IT Security Professionals Must Evolve for Changing Market“, SC Magazine, October 12, 2006.
- Aceituno, V., “On Information Security Paradigms“,ISSA Journal, September, 2005.
- Dhillon, G., “Principles of Information Systems Security: text and cases”, John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
11:09:00 PM
|
Labels:
information security,
information technology,
IT
|
- Internet
- Careers
- internet security
- web
- Networking
- ORT
- Operational Research
- Operations Research
- Proxy
- Tutorial
- PHP
- "Adding a Google Custom Search Engine "
- Assam
- DHCP
- E-Commerce
- FTP Upload via cURL
- Google Hacking
- IT
- Leisure
- Light
- Market and Survey Researchers
- Multiple Language Translation
- Open Proxy
- PHP/SQL Securiity
- Photography
- Proxy Server
- Reputation Management
- Reverse Proxy
- SQL
- cURL
- firewall
- information security
- information technology
- sudoku
2 comments:
Hello !
your blog is powerful
Thanks
I add this home page to may friend links in my blog.
if you don't want this please say me, else I happy you add my blog and link to me.
If you want add me in your blog please use this name: "HMB™ Softwares"
my blog:
http://hmbsoftwares.blogspot.com/
sorry for this post.
I can't find your mail!
Dear I followed a visitor and reached your blog dear.
You do write a lot and dear.., I was checking ICFAI and IGNOU sites for courses in Cyber Law. The former gives you around 1 year course for a PG diploma and the later offers a 6months stuff.. Not so sure of the outcome. :(
Pss.. mentioned the same coz seen some laws like data protection act(that was used a lot in my previous company when we were dealing with clients in UK.)
Post a Comment